Black pigments play a crucial role in various industries, from manufacturing to automotive and beyond. Understanding the differences between general black pigments and carbon black is essential for selecting the appropriate material for specific applications.
This article delves into the composition, applications, and solutions associated with black pigments and carbon black, providing a comprehensive comparison for industry professionals and decision-makers.
Definitions and Distinctions
What is Black Pigments:
Black pigments encompass a broad category of materials that impart black color to products. These pigments vary in chemical composition and origin, including natural sources like charcoal and synthetic variants like iron oxide-based blacks. Their diverse nature allows for a wide range of applications depending on the specific properties required.
What is Carbon Black:
Carbon black is a specialized form of carbon produced through the incomplete combustion of hydrocarbons. Unlike general black pigments, carbon black is engineered to possess specific properties such as high surface area, controlled particle size, and excellent dispersion characteristics. These attributes make carbon black a preferred choice in applications demanding superior performance.
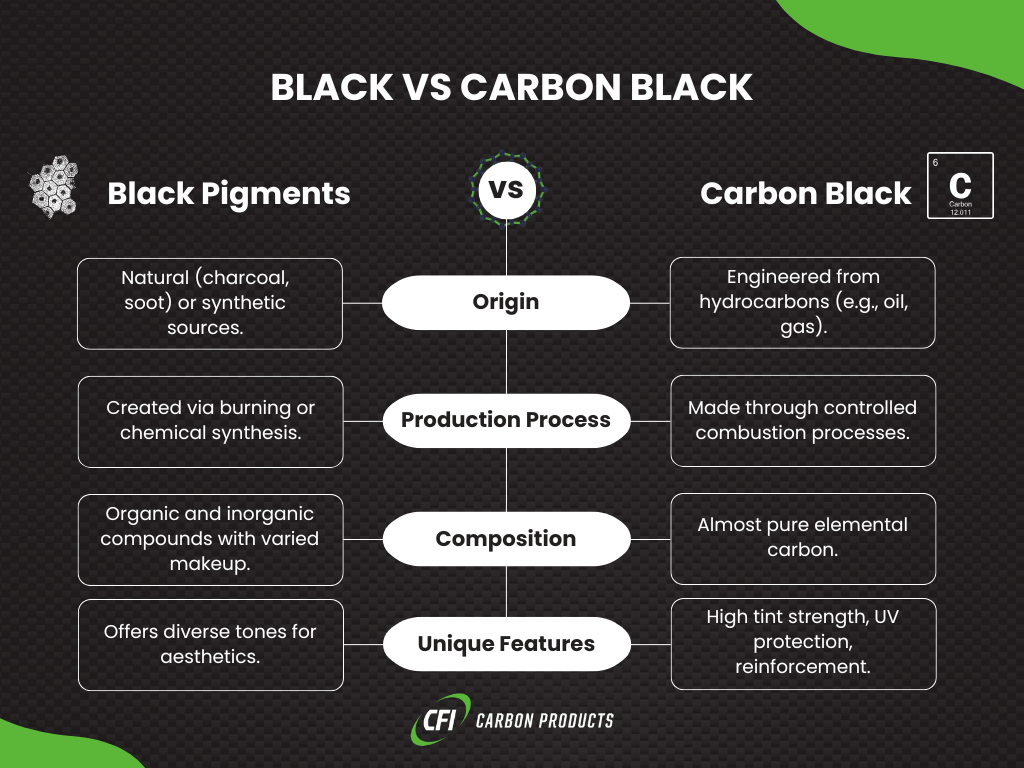
Composition and Production Processes (Black vs Carbon Black)
Black Pigments
Black pigments derive from both natural and synthetic sources, leading to varied chemical structures. Natural black pigments include charcoal and bone black, while synthetic options encompass pigments like lamp black and iron oxide black.
The production processes for these pigments can involve grinding natural materials or chemically synthesizing pigments to achieve desired properties.
Carbon Black
Carbon black is produced primarily through the furnace black process, which involves the thermal decomposition of hydrocarbons in a controlled environment.
This method yields carbon black with high carbon content and specific particle size distributions. The resulting material is characterized by its fine particulate structure and high surface area, distinguishing it from other black pigments.
| Aspect | Black Pigments | Carbon Black |
| Origin | Natural (e.g., charcoal) and synthetic sources | Engineered through incomplete combustion |
| Chemical Composition | Varied, including iron oxides and elemental carbon | Predominantly elemental carbon |
| Production Methods | Grinding natural materials or chemical synthesis | Furnace black process, thermal decomposition |
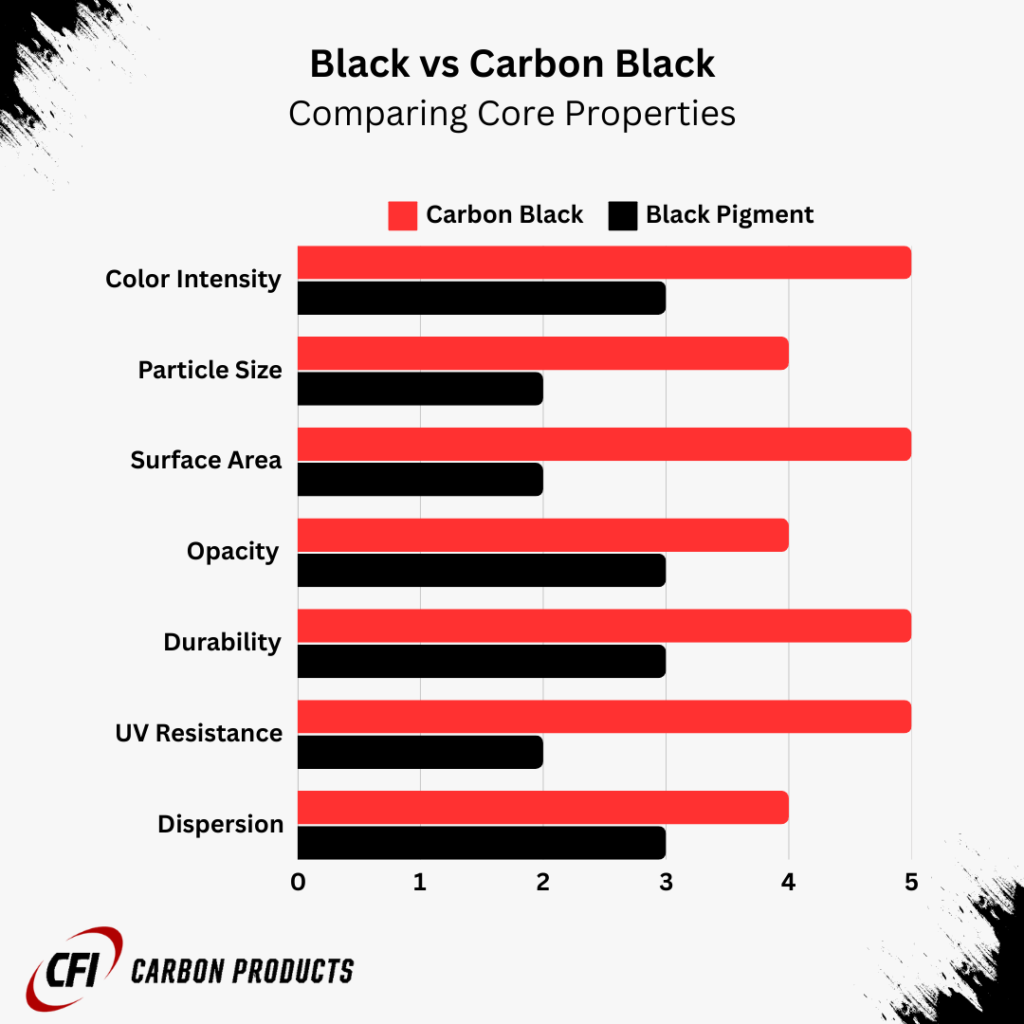
Physical and Chemical Properties (Black vs Carbon Black)
Color Intensity and Hue
Black pigments offer varying degrees of color intensity and undertones depending on their composition. For instance, iron oxide blacks may exhibit a slight brownish hue, while carbon black provides a deeper, more uniform blackness. The choice between these pigments can affect the final appearance of the product.
Particle Size and Surface Area
The particle size and surface area of pigments significantly influence their properties. Carbon black typically has a smaller particle size and higher surface area compared to general black pigments, enhancing tinting strength and dispersion. These characteristics are critical for applications requiring uniform color distribution and stability.
Opacity and Coverage
Opacity refers to the pigment’s ability to cover underlying layers. Carbon black generally offers higher opacity and better coverage, making it suitable for applications where complete color masking is essential. In contrast, some black pigments may require higher concentrations to achieve similar coverage levels.
| Property | Black Pigments | Carbon Black |
| Color Intensity | Variable, may have undertones | High, uniform blackness |
| Particle Size | Larger and varied | Smaller, more uniform |
| Surface Area | Lower compared to carbon black | Higher, enhancing dispersion |
| Opacity | Moderate to high depending on type | Generally higher, better coverage |
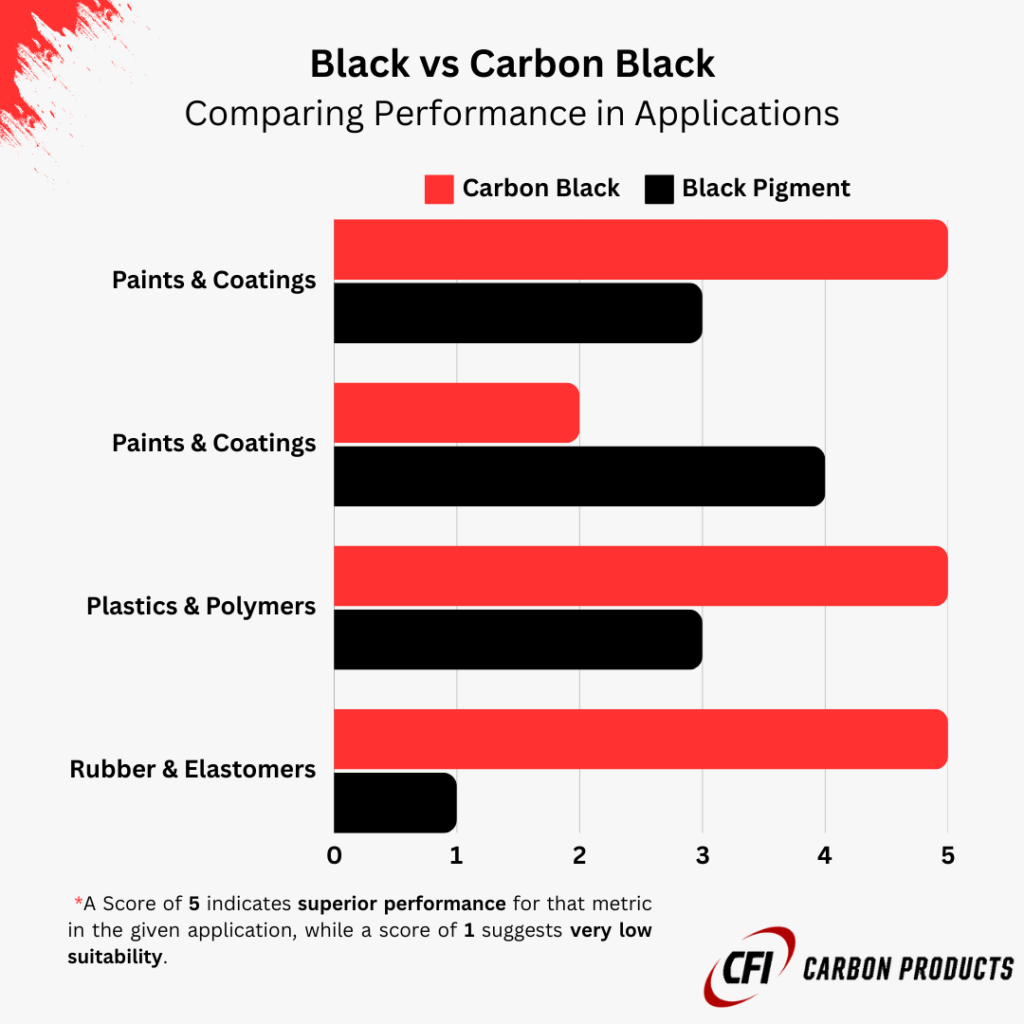
Industrial Applications (Black vs Carbon Black)
Paints and Coatings
In paints and coatings, black pigments and carbon black serve to provide color and protection. Carbon black is favored for its superior UV resistance and durability, resulting in finishes that maintain their appearance over time. General black pigments may be chosen for applications where cost-effectiveness is prioritized over long-term performance.
Plastics and Polymers
Black pigments and carbon black influence the mechanical properties and UV resistance of plastic products. Carbon black enhances the strength and longevity of plastics, making it ideal for automotive parts and consumer goods. Conversely, other black pigments might be used in less demanding applications where extensive reinforcement is not required.
Rubber and Elastomers
Carbon black is extensively used as a reinforcing agent in rubber products, significantly improving tensile strength and abrasion resistance. While other black pigments can color rubber, they do not provide the same level of reinforcement, limiting their use in high-performance applications.
| Application | Black Pigments | Carbon Black |
| Paints and Coatings | Cost-effective, variable durability | Superior UV resistance, enhanced durability |
| Plastics and Polymers | Suitable for basic coloration | Improves mechanical properties, UV resistance |
| Rubber and Elastomers | Limited reinforcement capabilities | Enhances tensile strength and abrasion resistance |
Performance Analysis (Black vs Carbon Black)
Durability and Weather Resistance
Products colored with carbon black exhibit greater durability and resistance to environmental factors such as UV radiation and oxidation. This makes carbon black ideal for outdoor applications and products exposed to harsh conditions. General black pigments may degrade more quickly under similar conditions, depending on their chemical stability.
Dispersion and Processing
Carbon black’s fine particle size and high surface area facilitate easier dispersion in various manufacturing processes, ensuring consistent color and performance. General black pigments, with their larger and more varied particle sizes, may require more intensive processing to achieve uniform dispersion, potentially increasing manufacturing complexity and costs.
| Performance Aspect | Black Pigments | Carbon Black |
| Durability | Variable, generally lower than carbon black | High durability and weather resistance |
| Weather Resistance | Susceptible to degradation in some cases | Excellent resistance to UV and oxidation |
| Dispersion | May require intensive processing | Easier dispersion due to smaller particle size |
| Processing Efficiency | Potentially higher processing requirements | Streamlined integration into manufacturing |
Environmental and Health Considerations
Black Pigments
The environmental and health impacts of black pigments vary based on their composition. Natural pigments like charcoal are generally less harmful, whereas synthetic pigments may involve hazardous chemicals during production and disposal. Proper handling and regulatory compliance are essential to mitigate potential risks.
Carbon Black
Carbon black production and use raise specific health and environmental concerns. Exposure to carbon black particles can pose respiratory risks, and its manufacturing process may result in emissions that require stringent environmental controls. Regulatory guidelines govern the safe handling and use of carbon black to minimize adverse effects.
“At CFI Carbon Products, we provide a distinctive alternative to carbon black that is less invasive and has lower CO2 emissions. Discover more about Austin Black 325 and its diverse applications across industries such as rubber, plastic, coatings, and silicone.”
| Consideration | Black Pigments | Carbon Black |
| Environmental Impact | Varies; natural pigments generally lower | Production emits pollutants; requires controls |
| Health Risks | Depends on the chemical composition | Respiratory hazards from particle exposure |
| Regulatory Compliance | Varies by pigment type | Strict guidelines for handling and use |
Cost Implications
Black Pigments
The cost of black pigments depends on their source and production method. Natural pigments like charcoal are typically less expensive but may offer limited performance benefits. Synthetic pigments can vary in cost based on their chemical complexity and the scalability of their production processes.
Carbon Black
Incorporating carbon black into products involves higher material costs compared to some general black pigments. However, the performance benefits, such as enhanced durability and mechanical properties, often justify the additional expense. Economies of scale and advancements in production technology can also influence the cost-effectiveness of carbon black.
| Cost Aspect | Black Pigments | Carbon Black |
| Material Cost | Generally lower, especially natural types | Higher due to specialized production |
| Performance Benefits | May require higher quantities for desired effect | Enhanced properties can offset higher costs |
| Economic Factors | Dependent on source and synthesis complexity | Influenced by production efficiency and scale |
Case Studies (Black Pigment & Carbon Black Usages)
Case Study 1: Automotive Paints
A leading automotive manufacturer sought to improve the longevity and appearance of its vehicle paints.
By switching from traditional black pigments to carbon black, the company achieved enhanced UV resistance and color stability. This change resulted in longer-lasting finishes and reduced the frequency of repainting, thereby increasing customer satisfaction and reducing maintenance costs.
Case Study 2: Plastic Manufacturing
A plastic goods producer faced challenges with product discoloration and reduced mechanical strength. After evaluating options, the company incorporated a carbon black alternative “Austin Black 325”, (which is more environmentally friendly & low in CO2 emissions) into its plastic formulations.
The addition of AB325 not only provided consistent coloration but also improved the tensile strength and UV resistance of the products. This led to higher-quality offerings and expanded market reach, demonstrating both environmental and economic benefits.
- Read More about the 2025 Standards & Certifications for Plastic Reinforcement.
Conclusion
In summary, distinguishing between general black pigments and carbon black is vital for optimizing product performance and manufacturing efficiency. While black pigments offer versatility and cost-effectiveness, carbon black provides superior durability, mechanical reinforcement, and environmental resistance. Selecting the appropriate pigment depends on the specific requirements of the application, balancing performance benefits with cost considerations.
Industry professionals are encouraged to consult with experts or suppliers, such as our CFI Carbon Products, to determine the best solutions tailored to their needs.

If you are an industry professional or a decision maker and wish to enhance your products with the right materials, contact us today to learn more about how our flagship products Austin Black 325 & Austin Black Eco can meet your specific needs in rubber, plastics, coatings, and silicone applications.
Let our experts guide you in making informed decisions that balance performance and sustainability. As we often say in the manufacturing process: Never miss out on the opportunity to optimize formulations—reach out now!

